Mick Hall
 Macron met key New Caledonian officials on Thursday [Ludovic Marin/Pool via AP Photo]
Macron met key New Caledonian officials on Thursday [Ludovic Marin/Pool via AP Photo]
Fears are growing that French security forces could remain indefinitely in New Caledonia after being sent to quell deadly violence this week over stalled moves towards full independence from France.
As France loses its grip on its colonial possession following recent debacles in West Africa, French President Emmanuel Macron flew into the Pacific Islands country on Thursday.
He was seeking a political solution with local parties following the eruption of protests and violence that included gun battles, which claimed the lives of two Gendarmes (French police) and four civilians.
Macron said a 3,000-strong force deployed from France would remain “as long as necessary,” emphasising a return to calm and security was “the absolute priority.”
He paid tribute to those killed in the violence before meeting with politicians and business representatives during a summit that included independence leaders.
Ahead of his visit, Macron faced anger from groups that hold his hubris responsible for the chaos. “Here comes the fireman after he set the fire!” Front de Liberation Nationale Kanak et Socialiste (FLNKS) of New Caledonia’s Jimmy Naouna, posted on X after Macron’s office announced his surprise visit.
In a further post, Naouna said Macron and those accompanying him on the visit, Overseas and Interior Minister Gerald Darmanin Darmanin and Armed Forces Minister Sébastien Locornu, had ignored calls for peaceful talks to resolve issues over self-determination for the island nation for months and that they could not be trusted anymore.
The trio responsible for the uprising. Turning deaf ears to our call for peaceful talks since they bulldozed through the 2021 referendum and now the eletoral bill. Not to be trusted anymore! https://t.co/2yHisK7p3Q
— Jimmy Naouna (@JNaouna) May 22, 2024
Approximately 1,000 more French security personnel were sent to the archipelago at the weekend, when France’s High Commissioner Louis Le Franc vowed in a televised address that “Republican order will be re-established, whatever the cost.” If separatists “want to use their arms, they will be risking the worst,” he added.
LeFranc said French security forces would stage “harassment” raids to reclaim territory held by pro-independence groups.
France’s Macron makes high-stakes visit to riot-struck New Caledonia: Noumea (AFP) –
President Emmanuel Macron on Wednesday flew to France’s Pacific territory of New Caledonia on a politically risky visit aiming to defuse a crisis after nine days of… https://t.co/4id5iXHYTB pic.twitter.com/sUtRUu264C
— zeta panama (@zetacompa) May 22, 2024
Start of Unrest
The crisis was sparked after France’s lower house, the National Assembly, on May 14 made changes to a 1998 agreement that had charted a path to decolonisation after decades of conflict.
Assembly bill will get rid of one of the agreement’s provisions by allowing residents who arrived in the country after 1998 to vote, shifting the balance of power away from the indigenous population and weakening their chances of winning independence via referendum.
The bill specifically makes constitutional changes removing electoral restrictions protecting the demographic status of the nation’s indigenous Kanaky people, as agreed under the Nouméa Accord.
The change, which followed a constitutional review initiated by Darmanin, would allow French nationals living on the island for at least 10 years to vote in local elections.
France retains a strategic and economic interest in the small Pacific nation of 270,000 residents, situated 750 miles (1200km) east of Australia. It is the third-largest exporter of nickel globally, while France is also attempting to reposition itself as a Western security partner in the Pacific.
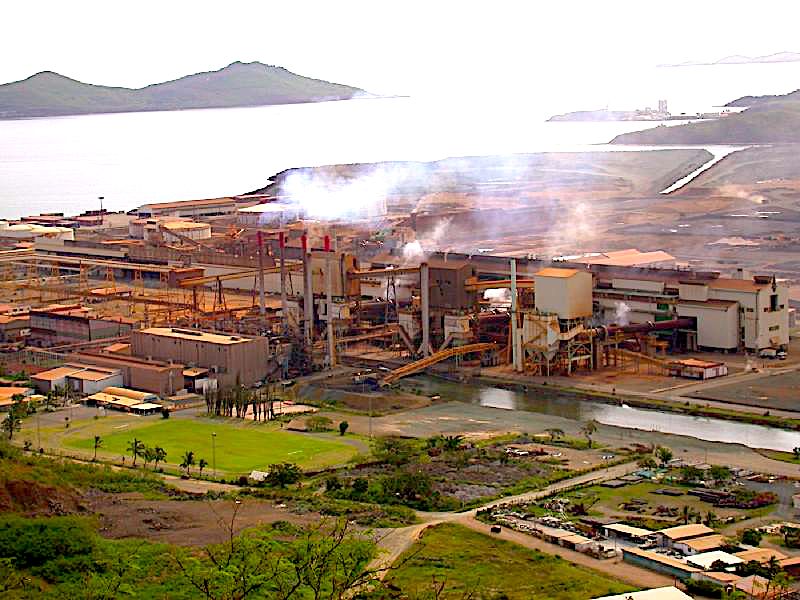

Nickel smelter in Nouméa, New Caledonia, 2006. (Tim Waters, Flickr, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
On Sunday, May 19 about 600 paramilitary police and army busted through approximately 70 barricades, which included dozens of burn-out vehicles, blocking a 64km stretch of road from the capital’s Nouméa to La Tontouta international airport. Some of the barricades were immediately re-erected.
A 6pm to 6am curfew remains in place until the end of a state of emergency on May 27. Disenfranchised youth have been responsible for most of the rioting. Tik Tok has also been banned and over 230 people have so far been arrested.
Both New Zealand and Australia began emergency repatriations using military aircraft from the Magenta airport, 4km outside the capital on Tuesday.
Macron has been accused of sparking the turmoil by imposing a colonial agenda on the country, running contrary to the Nouméa Accord.
Blaming Azerbaijan
French Interior Minister Gérald Darmanin has accused Azerbaijan, far from New Caledonia, of stirring up trouble there. “This isn’t a fantasy. It’s a reality,” he told French TV. “I regret that some of the Caledonian pro-independence leaders have made a deal with Azerbaijan. It’s indisputable,” he said.
He added: “Even if there are attempts at interference… France is sovereign on its own territory, and so much the better.”
Azerbaijan denied the allegation. “We completely reject the baseless accusations,” Azerbaijan’s foreign ministry spokesman Ayhan Hajizadeh said. “We refute any connection between the leaders of the struggle for freedom in Caledonia and Azerbaijan.”
Azerbaijan has been vocal in attacking French colonialism and invited pro- independence groups to Baku from several French dependencies in Polynesia for a conference towards the complete elimination of colonialism last July. It was organized by the Buku Initiative Group, which released a statement last week in solidarity with Kanaks resisting French reforms.
Follows French Losses in Africa
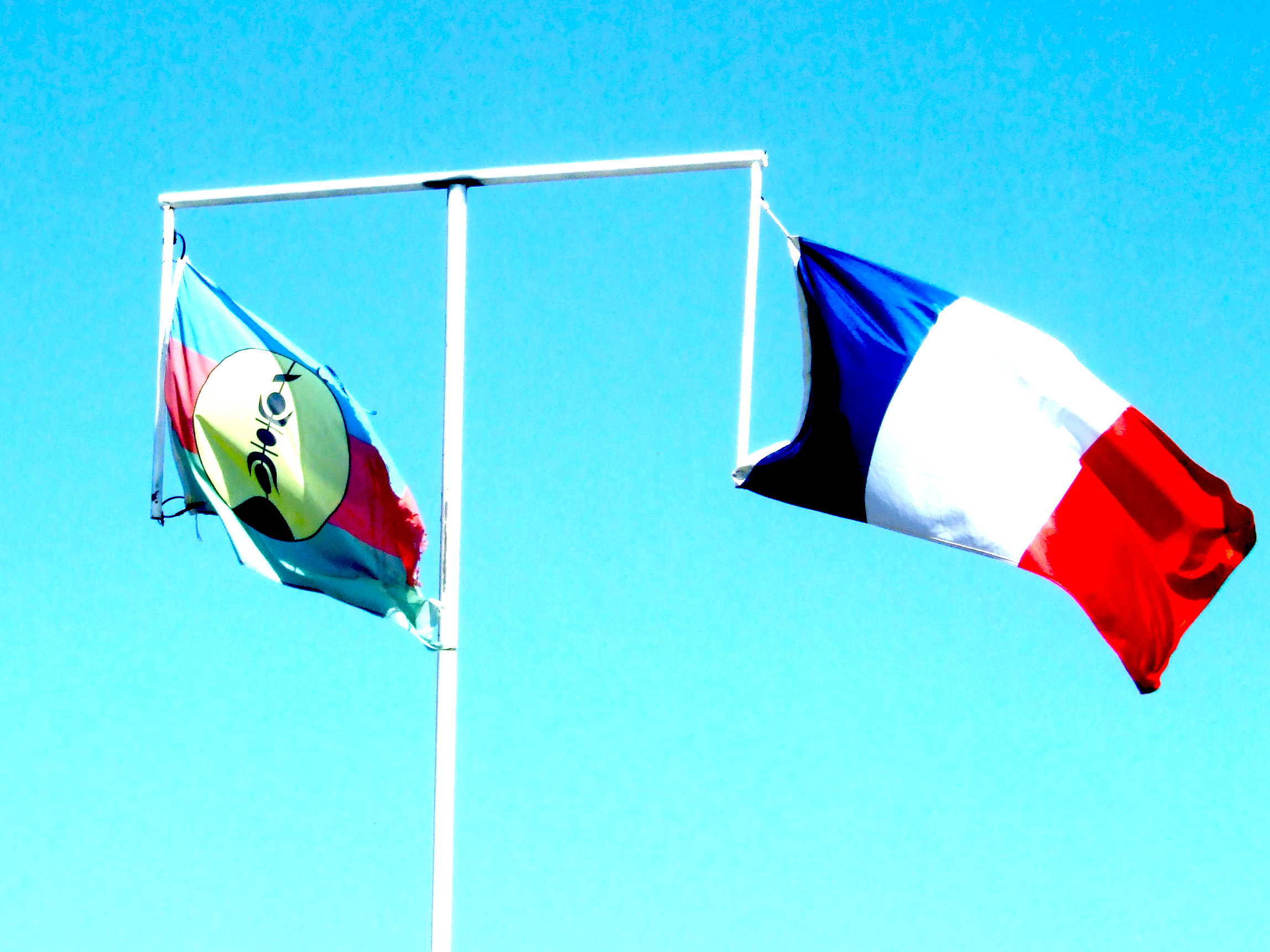

The French Tricolour and Kanak flag side by side, Nouméa, New Caledonia, March 2011. (BeenAroundAWhile, Wikimedia Commons, CC BY 3.0)
The uprising in New Caledonia follows unrest in the former French West Africa that forced French troops out of Niger, Mali and Burkina Faso last year. It cost France access to cheap uranium, especially from Niger, putting political pressure on Macron from powerful French interests. A loss of New Caledonia would not be welcomed in Paris as French colonial interests crumble.
Eddy Banare, a researcher in comparative literature with an interest in Kanak identity/political discourse at the Université de la Nouvelle-Calédonie, told Consortium News Macron and his government had demonstrated a serious lack of understanding of the New Caledonian issue and had failed to maintain a dialogue with local parties.
“The Nouméa Accord is based on an agreement between political actors in New Caledonia. This agreement has been compromised,” he said.
“Macron has aligned himself with the hardest right of the New Caledonian political spectrum, which, in its fervour to maintain a French New Caledonia, rejects the spirit of collegiality established by the Nouméa Accord by disregarding the Kanak independence claim and sabotaging the conditions for dialogue.”
Macron has had three meetings of his Defence and National Security Council within a week and his decision to send more troops is a reflection of a serious breakdown of order in New Caledonian society not seen since the 1980s.
“Everything seems to be set for the long term,” Banare said, adding that 100,000 firearms currently circulating in the country also needed to be taken out of the equation. Armed pro-France loyalist militias and anti-colonial groups have been active during the protests. Three of those killed were Kanaks, shot by armed civilians.
Banare said, in the absence of an impartial arbitrator, Australia and New Zealand should host roundtable talks, bringing together New Caledonian parties, a representation of the French government, and experts in international law and indigenous issues in the Pacific.
The Pacific Regional Non-Governmental Organisations Alliance (PRNGA) on Monday also urged the U.N. and Pacific leaders to mediate dialogue towards restoring “a just and peaceful transition.”
In a statement, the organisation criticised Macron for his “poorly hidden agenda to prolong colonial control over the territory” and for ignoring warnings by indigenous groups that the unilateral decision to impose electoral changes could end 30 years of relative peace in New Caledonia.
Map showing location of New Caledonia in Oceania. (TUBS, Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0)
“This week, as the United Nations Decolonisation Committee (C24) sits in Caracas, Venezuela, to hear updates on the list of non-self-governing territories to be decolonised, France imposes a state of emergency on Kanaky-New Caledonia and sends more troops to the Pacific territory to restore order,” it said.
“Ironically, its overtures for law and order and for peace are in stark contrast to the misuse of institutional processes to inflict violence on the Kanaky people, as evidenced by behaviour in Paris.”
The deaths and destruction of property have left many in the economically divided country wary and on edge. The conflict is having a serious impact on the fragile economy, as well as affecting medical and food supplies across the island.
Louis Lagarde, an associate professor of literature, language and social sciences at University of New Caledonia, said initiating talks among the local communities should be a priority.
“It is still too early to predict when troops will leave the archipelago,” he told Consortium News. “Their present role is to secure the airports, the port, gain and allow access to hospitals, preserve the last standing shops and their restocking, and free the blockades on the main roads. Patients under dialysis are at heavy risk, and so are other patients with heavy treatments, pregnant women and so on.”
He said: “One has to understand that the present New Caledonia government, with a pro-independence majority and president, as well as the customary senate president, have urged calm on multiple occasions, to no — or little — avail. As harsh as it seems, the presence of military and police reinforcements is still crucial.”
‘Don’t Care if They Live or Die’
Whakatane-based Kanak Rodney Pirini said youth at the forefront of the protests were profoundly marginalised, their positions made worse after Kanak people began moving into urban centres over past decades, particularly into the capital, where extremes of wealth and poverty were most pronounced.
Pirini, a former Union Calédonienne (UC) member (part of the Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front) who had been jailed several times during protests in the mid-1980s, said the destructiveness of last week’s protests was a reflection of that social reality.
“Forty years after I was protesting, you have a lot of young people in town, with no job, with nothing, living side by side with rich French people. One block could be rich people, 20 metres away you have a block of poor people. It’s crazy.
“Some young people don’t care if they live or die. It’s a problem.”
Colonial History

View over Noumea, capital of New Caledonia, 2009. (Pilettes, Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0)
France officially took possession of Kanaky, or New Caledonia, in 1853 and colonisation saw the Kanaks forced from their lands, resulting in several failed rebellions over the decades to come.
New Caledonia’s modern political trajectory towards decolonisation was put in motion after the Matignon-Oudinot Accords were signed in 1988 by Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front (FLNKS) leader Jean-Marie Tjibaou and leader of the anti-independence Rally for Caledonia in the Republic (RPCR) party, Jacques Lafleur and France. It was approved in a referendum by 80 percent of the electorate.
The agreement sought compromise and a peaceful settlement after a period of civil war and armed resistance to French rule.
FLNKS leaders Jean-Marie Tjibaou and Yeiwéné Yeiwéné were assassinated by FLNKS militants opposed to the peace deal less than a year later.
The Nouméa Accords recognised Kanaks as the indigenous peoples of Kanaky and set out mechanisms to address both historical wrongs and transfer governance powers from France.
Kanaks make up approximately 40 percent of New Caledonia’s population and the provisions to restrict voting to those resident in the country prior to 1998 were designed to keep Kanaks’ electoral strength while a peaceful transition towards independence unfolded.
A series of referendums on independence was proposed, the first of which took place in 2018, registering a 43.3 percent in favour of independence, followed by 46.7 percent vote in a 2020 referendum.
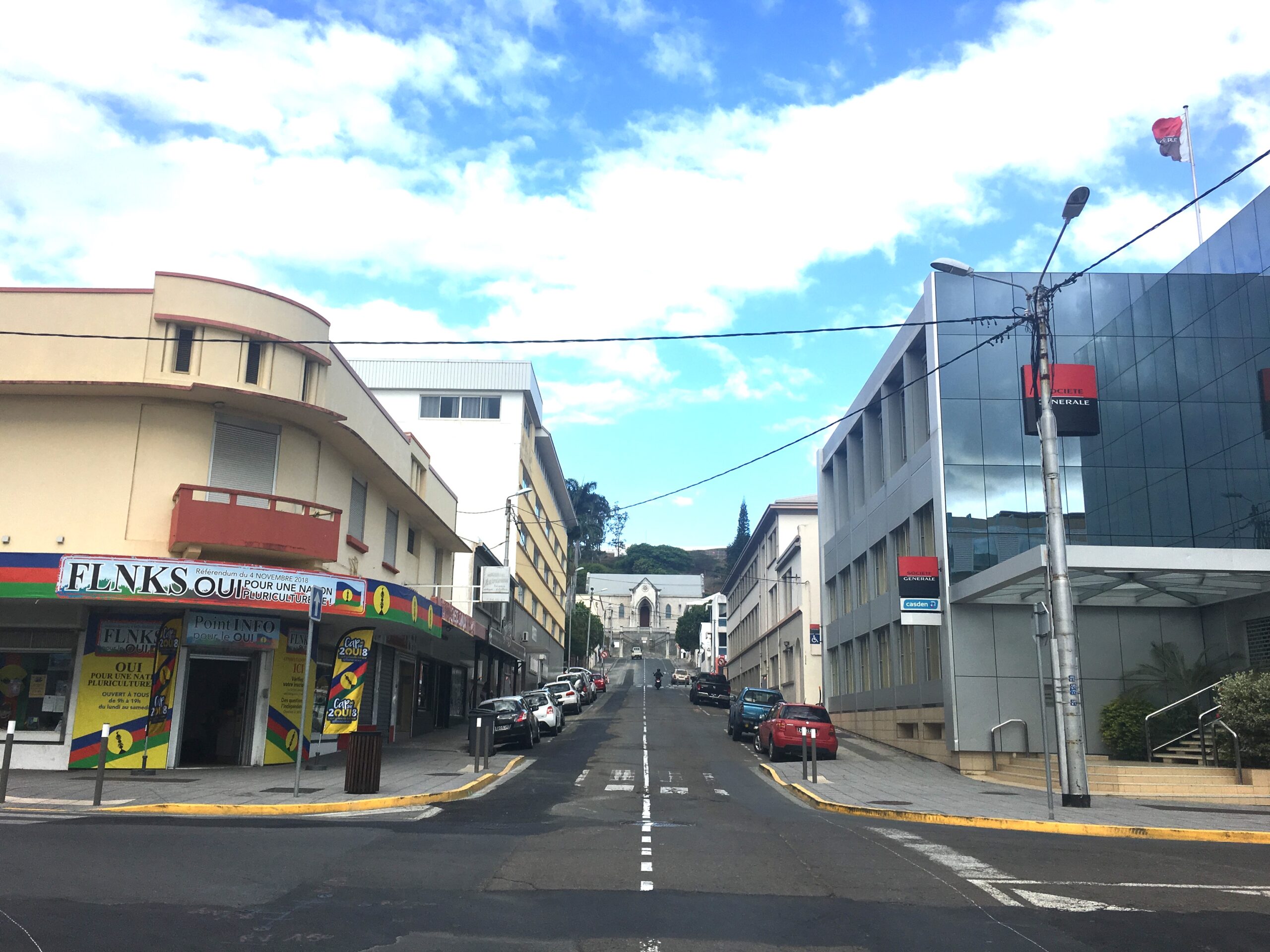

The FLNKS headquarters for the “yes” campaign in the 2018 referendum on the independence of New Caledonia, rue de l’Alma in Nouméa. (Marc Baronnet, Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The third referendum in December 2021 marked a slide towards today’s polarisation and is a key antecedent to the riots.
Calls for a postponement by independence parties after indigenous communities were hit hard by the Covid-19 Delta variant were ignored by France and the vote went ahead. After taking the issue to the U.N. Fourth Committee on Decolonisation, independence parties boycotted the referendum, resulting in a 44 percent voter turnout — or half of numbers that turned out in 2020. The vote delivered a mere 3.5 percent backing for independence.
Macron at the time hailed the vote as a “massive victory” for the pro-loyalist side. Pro-independence groups have been calling for another referendum.
Mick Hall is an independent journalist based in New Zealand. He is a former digital journalist at Radio New Zealand (RNZ) and former Australian Associated Press (AAP) staffer, having also written investigative stories for various newspapers, including the New Zealand Herald.